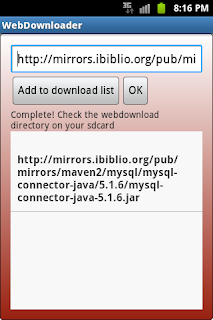
On the app user interface, we need one EditText, two Buttons, and one Listview. The EditText view allows the user to enter the address or url of the file to be downloaded. If the user selects a link from the browser, this text box will display the address or url of the link. The first Button labeled "Add to download list" is pushed to add the address in the text box to the ListView for later downloading. The second Button will be pushed to start the download process. It is labeled "OK". These views are defined in the activity_main.xml as shown below.
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:paddingBottom="@dimen/activity_vertical_margin"
android:paddingLeft="@dimen/activity_horizontal_margin"
android:paddingRight="@dimen/activity_horizontal_margin"
android:paddingTop="@dimen/activity_vertical_margin"
tools:context=".MainActivity"
android:orientation="vertical"
android:background="@drawable/back_style"
>
<EditText
android:id="@+id/txt_input"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:inputType="text"
android:hint="@string/txt_hint"
/>
<LinearLayout
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:orientation="horizontal"
>
<Button
android:id="@+id/bt_add"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="@string/bt_label"
android:onClick="addClick"
/>
<Button
android:id="@+id/bt_ok"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="@string/bt_ok"
android:onClick="okClick"
/>
</LinearLayout>
<TextView
android:id="@+id/txt_view"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
/>
<ListView
android:id="@+id/url_list"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="300dp"
android:paddingBottom="20dp"
android:paddingTop="20dp"
android:background="#f8f8f8"
/>
</LinearLayout>
To apply the backround to user interface, we need a resource file called back_style.xml stored in the drawable directory. This file defines the look and feel of the app background. To apply the background style to the user interface this file must be defined as a value of background property of the LinearLayout view (android:background="@drawable/back_style").
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<selector xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android">
<item>
<shape>
<gradient
android:startColor="#ffffff"
android:endColor="#992211"
android:angle="270" />
<stroke
android:width="1dp"
android:color="#171717" />
<corners
android:radius="4dp" />
<padding
android:left="10dp"
android:top="10dp"
android:right="10dp"
android:bottom="10dp" />
</shape>
</item>
</selector>
Some string resources that are used by the views are written in the strings.xml file. The content of the strings.xml file is shown below.
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<resources>
<string name="app_name">WebDownloader</string>
<string name="action_settings">Settings</string>
<string name="bt_label">Add to download list</string>
<string name="txt_hint">Enter web page address</string>
<string name="bt_ok">OK</string>
</resources>
As mentioned above, the user can launch the web downloader app by two ways. One is by selecting a link from the browser and another is by launching it directly from the Android applications laucher. For the first way, the web downloader app needs to be listed in the app choices list to view or download the file that is refered to by the link. You can have your apps to diplay in the popup list by defining intent filters in the AndroidManifest.xml file of the app. The intent filters specify the capacity that the web downloader app can do in terms of actions to be performed, and data to operate on. By doing this, the Android system know how to capture intents that match the capacity of the app and ignore intents that do not match. An intent is a data structure that contains data and operations on the data. It can be used to send and receive data in an app or between apps.
To define an intent filter, you need to use the <intent_filter> tag. This tag will be placed in the activity, service, or broadcast receiver that will receive the intent. When defining an intent filter, there are three parts that need to be considered. The first part specifies the action the app can do. In this example app, the action that the app can do is VIEW action. The VIEW action tells the Android that the web downloader app can download and display the content of the link. When this action is specified, the intent will contain the address or url of the link and so we can write code to get the link and download data from the link. The code to do these tasks are written in the MainActivity.java file that is shown later in this post. The second part determines the kind of the intents that will be received by the web downloader appp. The DEFAULT category allows the Android system to capture intents that do not have a category. In most cases, we use this category. The BROWABLE category tells Android to filter intents that are in browsable category (displayable and downloadable). The final part can be used to specify the type of data, or url (including scheme, host, and file path). In this app, we allow any file to be downloaded so the type of data can be specified by a value of "*/*" to the mimeType property. Sine the file to be downloaded is from the internet and from any host, the value of the scheme property will be "http" and the value for the host is "*".
<intent-filter>
<action android:name="android.intent.action.VIEW"></action>
<category android:name="android.intent.category.DEFAULT"></category>
<category android:name="android.intent.category.BROWSABLE"></category>
<data android:mimeType="*/*" android:scheme="http" android:host="*"></data>
</intent-filter>
For reference documentation about defining intent filter and its related parts, you can visit android developer website.
In this example app, the AndroidManifest.xml looks like the following.
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<manifest xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
package="com.example.webdownloader"
android:versionCode="1"
android:versionName="1.0" >
<uses-sdk
android:minSdkVersion="8"
android:targetSdkVersion="17" />
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.INTERNET"/>
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.ACCESS_NETWORK_STATE"/>
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.WRITE_EXTERNAL_STORAGE"/>
<application
android:allowBackup="true"
android:icon="@drawable/wd"
android:label="@string/app_name"
android:theme="@style/AppTheme" >
<activity android:configChanges="orientation"
android:name="com.example.webdownloader.MainActivity"
android:label="@string/app_name" >
<intent-filter>
<action android:name="android.intent.action.MAIN" />
<category android:name="android.intent.category.LAUNCHER" />
</intent-filter>
<intent-filter>
<action android:name="android.intent.action.VIEW"></action>
<category android:name="android.intent.category.DEFAULT"></category>
<category android:name="android.intent.category.BROWSABLE"></category>
<data android:host="*" android:scheme="http"></data>
</intent-filter>
</activity>
<service
android:name="DownloadService"
android:icon="@drawable/ic_launcher"
android:label="MYSERVICE">
</service>
</application>
</manifest>
In the AndroidManifest.xml file we also define the permissions for the web downloader app. The first permision allows the app to use the internet, the second permision to access the network connection states, and the final permision to read and write data to the external storage (sdcard).
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.INTERNET"/>
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.ACCESS_NETWORK_STATE"/>
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.WRITE_EXTERNAL_STORAGE"/>
The last part of the AndroidManifest.xml file, we declare a service. The name of the service is the same as the class that extends the Service or IntentService. A service can be used to do operations that need long time to complete. When doing long-time operations, the user interface is locked. So it does not respond to the user and this situation might make the user feel uncomfortable with your app. To avoid this problem, the operations need to be run in background. The IntentService class is used to do the downloading process in background in the web downloader appp because it can take long time to complete. A service can receive data (stored in an intent object) from an activity that requires the long-time process to be passed to the service and send the feedback information to the activity. In this app, the data to be sent from the main activity are the ArrayList object that store the urls of the links that were added to the ListView to download and the output directory to store the files downloaded. You need to override the onHandleIntent method to get the data stored in an intent object that is sent by the main activity.
DownloadService.java file
package com.example.webdownloader;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.net.HttpURLConnection;
import java.net.MalformedURLException;
import java.net.URL;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import android.app.IntentService;
import android.content.Intent;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.util.Log;
public class DownloadService extends IntentService {
private ArrayList<String> urlist;
private String storeDir;
public DownloadService() {
super("SERVICE");
// TODO Auto-generated constructor stub
}
public void onHandleIntent(Intent intent){
Bundle b=intent.getExtras();
if(b!=null){
urlist=b.getStringArrayList("URLS");
storeDir=b.getString("OUTDIR");
startDownload();
}
}
public void startDownload(){
String feedback="";
if(urlist.size()>0){
try {
for(int i=0;i<urlist.size();i++){
URL url=new URL(urlist.get(i));
readDataStream(url);
}
feedback="Complete! Check the webdownload directory on your sdcard";
} catch (MalformedURLException e) { e.printStackTrace();}
}
else{
feedback="No url is added to the download list.";
}
//send feedback message to the main activity
Intent backIntent=new Intent("com.example.webdownloader");
backIntent.putExtra("BACKMESS", feedback);
sendBroadcast(backIntent);
}
public void readDataStream(URL url){
try {
File f=new File(storeDir);
if(f.exists()){
HttpURLConnection con=(HttpURLConnection)url.openConnection();
InputStream is=con.getInputStream();
String path=url.getPath();
String filename=path.substring(path.lastIndexOf('/')+1);
FileOutputStream fos=new FileOutputStream(storeDir+"/"+filename);
int data=0;
while((data=is.read())!=-1){
fos.write(data);
}
is.close();
fos.flush();
fos.close();
}
else
Log.e("Error","Not found "+storeDir);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
To download content of a file that is refered to by a link, you can use the HttpURLConnection class. You can have HttpURLConnection object by using the openConnection method of the URL class.
HttpURLConnection con=(HttpURLConnection)url.openConnection();
HttpURLConnection class has the getInputStream method that returns an InputStream object. When you have the InputStream object, you can use its read method to read content of the file and write it to an output file by using the FileOutputStream class.
The final part of the web downloader app is MainActivity.java file. In this file, we use the ArrayList to store the addresses or urls that are added to the ListView. To use the ArrayList object as an datasource of the ListView, you need to create an ArrayAdapter object to encaptulate the ArrayList object. When creating the ArrayAdapter object you need to provide three values: context, layout of the ListView, and the ArrayList object. Then supply this adapter object to the ListView by using its setAdapter method.
aa=new ArrayAdapter<String>(this,R.layout.listlayout,urlist);
lv.setAdapter(aa);
The layout of the ListView view is defined in the listlayout.xml file in res/layout directory.
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<!-- Single List Item Design -->
<TextView xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:id="@+id/label"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="fill_parent"
android:padding="10sp"
android:textSize="16sp"
android:textStyle="bold" >
</TextView>
MainActivity.java file
package com.example.webdownloader;
import java.io.File;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import android.net.Uri;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.os.Environment;
import android.app.Activity;
import android.content.BroadcastReceiver;
import android.content.Context;
import android.content.Intent;
import android.content.IntentFilter;
import android.util.Log;
import android.view.Menu;
import android.view.View;
import android.widget.ArrayAdapter;
import android.widget.Button;
import android.widget.EditText;
import android.widget.ListView;
import android.widget.TextView;
public class MainActivity extends Activity {
private ListView lv;
private ArrayList<String> urlist;
private ArrayAdapter<String> aa;
private String storeDir;
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
urlist=new ArrayList<String>();
aa=new ArrayAdapter<String>(this,R.layout.listlayout,urlist);
lv=(ListView)findViewById(R.id.url_list);
lv.setAdapter(aa);
Intent intent=getIntent();
String action=intent.getAction();
if(Intent.ACTION_VIEW.equals(action)){
Uri uri=intent.getData();
EditText txturl=(EditText)findViewById(R.id.txt_input);
txturl.setText(uri.toString());
}
}
protected void onStart(){
super.onStart();
createStoreDir();
}
protected void onResume(){
super.onResume();
registerReceiver(receiver, new IntentFilter("com.example.webdownloader"));
}
protected void onPause(){
super.onPause();
unregisterReceiver(receiver);
}
private BroadcastReceiver receiver=new BroadcastReceiver(){
public void onReceive(Context context,Intent intent){
Bundle b=intent.getExtras();
if(b!=null){
TextView tv=(TextView)findViewById(R.id.txt_view);
tv.setText(b.getString("BACKMESS"));
}
}
};
public void createStoreDir(){
storeDir=Environment.getExternalStorageDirectory()+"/webdownload";
File f=new File(storeDir);
if(!f.exists())
if(!f.mkdir()){
Log.e("Error","Can't create webdownload directory");
disableButtons();
}
}
public void disableButtons(){
Button btadd=(Button)findViewById(R.id.bt_add);
Button btok=(Button)findViewById(R.id.bt_ok);
btadd.setEnabled(false);
btok.setEnabled(false);
}
public boolean onCreateOptionsMenu(Menu menu) {
// Inflate the menu; this adds items to the action bar if it is present.
getMenuInflater().inflate(R.menu.main, menu);
return true;
}
public void addClick(View view){
EditText txturl=(EditText)findViewById(R.id.txt_input);
String url=txturl.getText().toString();
if(url.length()>0){
urlist.add(url);
aa.notifyDataSetChanged();
}
}
public void okClick(View view){
TextView tv=(TextView)findViewById(R.id.txt_view);
tv.setText("Please wait...");
Intent newIntent=new Intent(this,DownloadService.class);
newIntent.putStringArrayListExtra("URLS", urlist);
newIntent.putExtra("OUTDIR",storeDir);
startService(newIntent);
}
}
The Intent object (called intent) can be obtained by using the getIntent method of the Activity class. This intent object contains the url of the selected link. To get the url from the intent object, you need to use the getData method of the Intent class.
Intent intent=getIntent();
String action=intent.getAction();
if(Intent.ACTION_VIEW.equals(action)){
Uri uri=intent.getData();
//more code here
}
To receive feedback message from the Service (DownloadService), the MainActivity needs to register a BroadcastRecevier by using the registerReceiver method when the activity starts.
registerReceiver(receiver, new IntentFilter("com.example.webdownloader"));
The receiver can be unregistered by using the unregisterReceiver method. This code fragment is usually placed in the onPause or onStop mehtod of the activity.
unregisterReceiver(receiver);
In the onReceive method of the BroadcastReceiver class, you can write some code to get the feedback message sent by the Service (stored in the intent object). The intent object has a method called getExtra that returns a Bundle object that the message is stored.
Bundle b=intent.getExtras();
if(b!=null){
TextView tv=(TextView)findViewById(R.id.txt_view);
tv.setText(b.getString("BACKMESS"));
}
When the user clicks the Add to download list button, the addClick method is called to add the address shown in the text box to the ArrayList and the ListView. When the OK button is pushed and the okClick method is called, the main activity sends an intent object that contains the ArrayList and output directory to the DownloadService. In this case, the intent object is constructed by specifying the context and the service class to start (DownloadService). Then you can call the startService to start the service.
Intent newIntent=new Intent(this,DownloadService.class);
newIntent.putStringArrayListExtra("URLS", urlist);
newIntent.putExtra("OUTDIR",storeDir);
startService(newIntent);
Now run the web downloader app. Then upload and install the WebDownload.apk to your real device. In your real device, make sure the internet is working. Start your web browser and find a download link. Select the download link and choose WebDownloader from the popup list. When the address of the download link shown in the text box, select the Add to download list button to add the address to the ListView then click the OK button.
Download apk file of the Web Downloader app


No comments:
Post a Comment